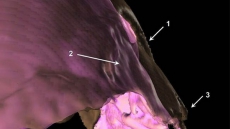
A new laser 3D scan of the extinct flightless bird dodo has exposed portions of its anatomy previously unknown to science, revealing secrets about how the bird once lived, says a study.
The dodo, a flightless bird about three feet tall, was native to Mauritius and went extinct by 1693 - less than a century after the Dutch discovered the island in 1598.
"We discovered that the anatomy of the dodo we were looking at was not described in detail," Leon Claessens, vertebrate paleontologist at the College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, Massachusetts, was quoted as saying in a Live Science report.
There were bones of the dodo, such as its kneecaps, which were unknown to science until now, Leon noted.
"The skull of the dodo is so large and its beak so robust that it is easy to understand that the earliest naturalists thought it was related to vultures and other birds of prey, rather than the pigeon family," said co-author Hanneke Meijer from the Catalan Institute of Paleontology, Spain.
For their study, Claessens and colleagues used a laser scanner to create a 3D digital model of the specimen.
"The 3D laser surface scans we made of the fragile Thirioux dodo skeletons enabled us to reconstruct how the dodo walked, moved and lived to a level of detail that has never been possible before," concluded Claessens.
The findings were recently presented at the annual meeting of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology in Berlin.