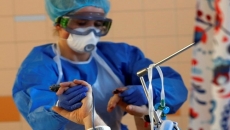
A small study strengthens evidence that a pregnant woman infected with the coronavirus might be able to spread it to her fetus.
Researchers from Italy said Thursday that they studied 31 women with COVID-19 who delivered babies in March and April. They found signs of the virus in several samples of umbilical cord blood, the placenta and, in one case, breast milk.
Women shouldn’t panic. This doesn’t mean there’s viable virus in those places and “it’s too early to make guidelines” or to change care, said the study leader, Dr. Claudio Fenizia, an immunology specialist at the University of Milan.
But it does merit more study, especially of women who are infected earlier in their pregnancies than these women, said Fenizia, who discussed the results at a medical conference being held online because of the pandemic.
Since the start of the pandemic, doctors have wondered whether in-the-womb infection could occur. HIV, Zika and some other viruses can infect a fetus this way. Several early reports from China suggested the coronavirus might, too, although doctors suspect those women may have spread the virus to their babies during or after birth.
The new study involved women at three hospitals during the height of the outbreak in northern Italy. The virus’s genetic material was found in one umbilical cord blood sample, two vaginal swabs and one breast milk sample. Researchers also found specific, anti-coronavirus antibodies in umbilical cord blood and in milk.
In one case, “there’s strong evidence suggesting that the newborn was born already positive because we found the virus in the umblilical cord blood and in the placenta,” Fenizia said.
In another case, a newborn had antibodies to the coronavirus that do not cross the placenta, so they did not come from the mother and were “due to direct exposure of the fetus to the virus,” Fenizia said.
In any case, the possibility of fetal infection seems relatively rare, he said. Only two of the newborns tested positive for the coronavirus at birth and neither became ill from it.
Dr. Ashley Roman, a pregnancy specialist at NYU Langone Health, said she and colleagues also detected viral particles on the fetal side of the placenta in several of the 11 cases they examined. The new report adds evidence that in-womb transmission is possible, but it seems rare and to not cause serious problems in the infants, she said.
“The most important thing that pregnant women need to know is it’s important to socially distance. It’s important to wear a mask, wash their hands,” Roman said. "Women don’t need to be cut off from society entirely, but they should be concerned about the impact of getting COVID on their own health during pregnancy."
Dr. Anton Pozniak, a conference leader and virus expert at the Chelsea and Westminster Hospital in London, said the implications of the Italian research “have to be worked out.”
Children under age 3 rarely get seriously ill from coronavirus, and “I would suspect that even if there was transmission to babies, it was not harmful,” he said.
UNICEF, the United Nations’ children’s agency, recommends that new moms with COVID-19 wear a mask while breastfeeding, he added.